-
단순선형회귀 방법 1, 방법 2 예제(Sequential api, Function api)TensorFlow 2022. 11. 30. 15:31

방법1
import tensorflow as tf from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Activation from keras import optimizers import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.metrics import r2_score from keras.optimizers import SGD, RMSprop, Adam df = pd.read_table('http://www.randomservices.org/random/data/Galton.txt') df = df.loc[(df['Gender'] == 'M')].drop('Gender', axis=1) print(df.head(3)) x = df['Father'] y = df['Height'] print(x[:3]) print(y[:3]) print(np.corrcoef(x, y)) # 0.391 # train / test split (7 : 3) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 0) print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape) # (325,) (140,) (325,) (140,) model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(units=5, input_dim=1, activation='linear')) model.add(Dense(units=1, activation='linear')) print(model.summary()) opti = optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.01) model.compile(optimizer=opti, loss='mse', metrics=['mse']) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=4, epochs=100, verbose=0) loss_metrics = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0) print('loss_metrics :', loss_metrics) print('설명력 :', r2_score(y_test, model.predict(x_test))) print('실제값 :', y_test[:5].values) print('예측값 :', model.predict(x_test).flatten()[:5]) # 새로운 값 예측 new_height = [75, 70, 80] print('새로운 예측값: ', model.predict(new_height).flatten()) # 시각화 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rc('font', family='malgun gothic') plt.plot(x_train, model.predict(x_train), 'b', x_test, y_test, 'ko') # train plt.show() plt.plot(x_test, model.predict(x_test), 'b', x_test, y_test, 'ko') # test plt.show() plt.plot(history.history['mse'], label='평균제곱오차') plt.xlabel('학습 횟수') plt.show() <console> Family Father Mother Height Kids 0 1 78.5 67.0 73.2 4 4 2 75.5 66.5 73.5 4 5 2 75.5 66.5 72.5 4 0 78.5 4 75.5 5 75.5 Name: Father, dtype: float64 0 73.2 4 73.5 5 72.5 Name: Height, dtype: float64 [[1. 0.39131736] [0.39131736 1. ]] (325,) (140,) (325,) (140,) Model: "sequential" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= dense (Dense) (None, 5) 10 dense_1 (Dense) (None, 1) 6 ================================================================= Total params: 16 Trainable params: 16 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ None loss_metrics : [13.743265151977539, 13.743265151977539] 1/5 [=====>........................] - ETA: 0s 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 500us/step 설명력 : -1.0972842836983117 실제값 : [68. 67. 70. 67. 70.2] 1/5 [=====>........................] - ETA: 0s 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 997us/step 예측값 : [67.28584 70.39301 72.14079 73.111786 69.22783 ] 1/1 [==============================] - ETA: 0s 1/1 [==============================] - 0s 53ms/step 새로운 예측값: [76.99574 72.14079 81.85071] 1/11 [=>............................] - ETA: 0s 11/11 [==============================] - 0s 708us/step 1/5 [=====>........................] - ETA: 0s 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 748us/step방법2
print('\n--Function api 사용------------------------------') from keras.layers import Input from keras.models import Model inputs = Input(shape=(1,)) output1 = Dense(units=5, activation='linear')(inputs) outputs = Dense(1, activation='linear')(output1) model2 = Model(inputs, outputs) print(model2.summary()) opti = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.001) model2.compile(optimizer=opti, loss='mse', metrics=['mse']) history = model2.fit(x=x_train, y=y_train, epochs=50, batch_size=4, verbose=0) loss_metrics2 = model2.evaluate(x=x_test, y=y_test, verbose=0) print('loss metrics: ', loss_metrics2) print('실제값 : ', y_test.head().values) print('예측값 :', model2.predict(x_test).flatten()[:5]) print() new_data = [75, 70, 80] print('새로운 예측 키 값: ', model2.predict(new_data).flatten()) <console> --Function api 사용------------------------------ Model: "model" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 1)] 0 dense_2 (Dense) (None, 5) 10 dense_3 (Dense) (None, 1) 6 ================================================================= Total params: 16 Trainable params: 16 Non-trainable params: 0 _________________________________________________________________ None loss metrics: [8.111572265625, 8.111572265625] 실제값 : [68. 67. 70. 67. 70.2] 1/5 [=====>........................] - ETA: 0s 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 748us/step 예측값 : [65.24897 68.451355 70.2527 71.25345 67.25046 ] 1/1 [==============================] - ETA: 0s 1/1 [==============================] - 0s 50ms/step 새로운 예측 키 값: [75.25643 70.2527 80.26017]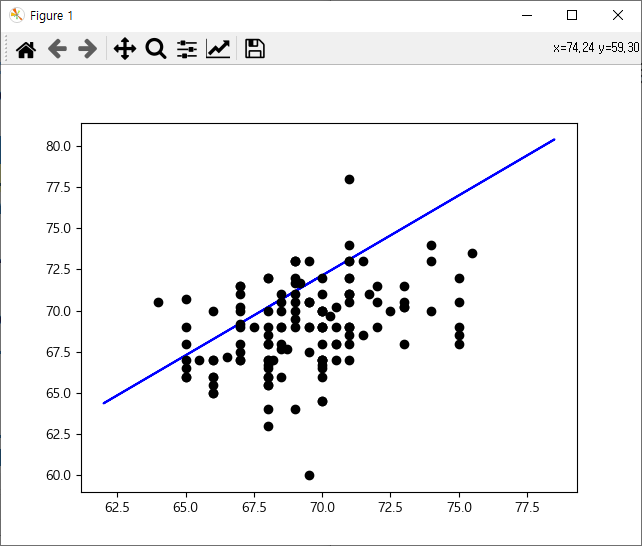
train 시각화 
test 시각화 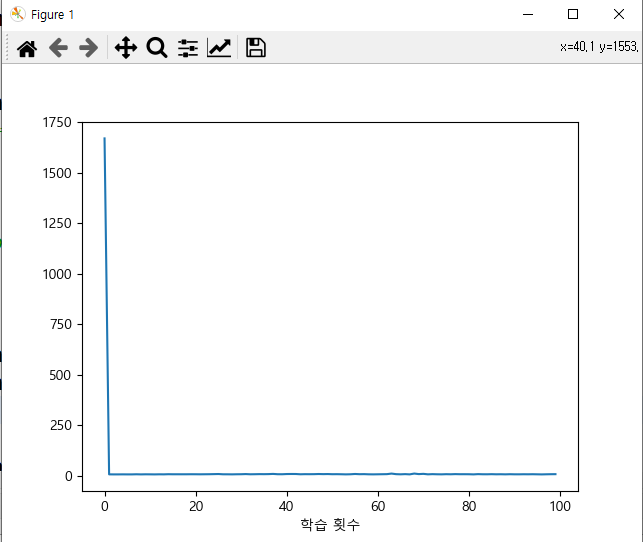
'TensorFlow' 카테고리의 다른 글
TensorFlow 기초 13 - 다중선형회귀모델(scaling) - 정규화, 표준화 validation_split (0) 2022.11.30 TensorFlow 기초 12 - 다중선형회귀모델 작성 후 텐서보드(모델의 구조 및 학습과정/결과를 시각화) - (0) 2022.11.30 TensorFlow 기초 11 - 단순선형회귀모델 작성 : 방법 3가지(다중 입출력 모델) (0) 2022.11.30 TensorFlow 기초 10 - 선형회귀분석 예제(예측, 결정계수) (0) 2022.11.30 TensorFlow 기초 9 - 선형회귀 모형 작성 = 수식 사용(Keras 없이 tensorflow만 사용) - GradientTape (0) 2022.11.29